Compressibility equation
In statistical mechanics and thermodynamics the compressibility equation refers to an equation which relates the isothermal compressibility (and indirect the pressure) to the structure of the liquid. It reads:
![kT\left(\frac{\partial \rho}{\partial p}\right)=1%2B\rho \int d r [g(r)-1]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/7398478c87fd42d409c1fda60f0c2b07.png) (1)
(1)
where 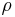 is the number density, g(r) is the radial distribution function and
is the number density, g(r) is the radial distribution function and 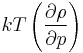 is the isothermal compressibility.
is the isothermal compressibility.
Using the Fourier representation of the Ornstein-Zernike equation the compressibility equation (1) can be rewritten in the form:
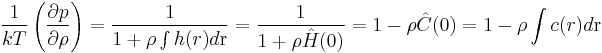 (2)
(2)
where h(r) and c(r) are the indirect and direct correlation functions respectively. The compressibility equation is one of the many integral equations in statistical mechanics.
References
- D.A. McQuarrie, Statistical Mechanics (Harper Collins Publishers) 1976